In our home, plants are decorative objects that bring beauty and vitality. However, it is essential to know that some of these plants can pose a danger to our pets. In this blog, we present you with a detailed list of 40 common indoor and outdoor toxic plants. We want to help you identify these plants and know the associated risks so you can take preventative measures to protect your cat and dog from possible poisoning.
Each plant mentioned includes information about its toxicity, the parts of the plant that are dangerous and the symptoms they can cause in case of ingestion or contact, and we also provide you with photos to make it easier for you to recognize them.
Indor toxic plants
- Dieffenbachia (“Leopard Lily” or “Dumb Cane”)
- Epipremnum aureum (“Pothos” or “Devil’s Ivy”)
- Philodendron
- Spathiphyllum (Peace Lily)
- Anthurium (“Flamingo flower” or “Tailflower”)
- Caladium
- Monstera (“Swiss Cheese Plant”)
- Zamioculcas zamiifolia (“ZZ plant or “Aroid Palm”)
-
- Toxicity: Calcium oxalate.
- Toxic part: whole plant.
- Symptoms: May cause symptoms such as severe irritation of the mouth, lips, tongue and throat with a burning sensation in the mouth and difficulty in swallowing due to possible swelling. In addition, it may cause nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. In less common situations, it may also cause respiratory problems due to swelling of the airways.

- Ficus, the most common (Weeping Fig and Rubber Plant)
- Toxicity: salvia (latex)
- Toxic part: the whole plant.
- Symptoms: May cause skin irritation, allergic reactions such as dermatitis, and redness. If swallowed, it may cause irritation to the mouth and stomach, accompanied by abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting. Contact with eyes causes severe irritation, pain and redness.
- Euphorbia (more than 2000 species, many of them toxic)
- Toxicity: salvia (latex)
- Toxic part: the whole plant.
- Symptoms: Local exposure may produce skin and mucous membrane irritation, allergic reactions, skin irritant dermatitis or a corrosive effect, depending on the Euphorbia species. Ingestion of some Euphorbia species may produce gastrointestinal symptoms such as gastric pain, nausea, retching, laxative action and bloody diarrhea.
- Codiaeum variegatum (Croton)
- Toxicity: diterpenes and phorbol esters.
- Toxic part: whole plant.
- Symptoms: May cause skin irritation, redness and blistering. If ingested, may cause mouth and throat irritation, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. In addition, contact with eyes may cause severe irritation.
- Dendranthema (Chrysanthemum)
- Toxicity: Pyrethrins.
- Toxic part: whole plant.
- Symptoms: May cause dermatitis or skin irritation, especially in sensitive individuals. Ingestion of the plant may lead to gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, as well as possible oral irritation. Eye contact may cause irritation.
- Amaryllis (Hippeastrum)
- Clivia Miniata (St. Joseph Lily)
- Toxicity: Licorin
- Toxic part: whole plant, especially bulbs.
- Symptoms: ingestion may cause vomiting, nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain, and in severe cases, depression of the central nervous system, leading to lethargy or convulsions. Skin contact may, in rare cases, cause dermatological irritation in sensitive dogs and cats.
- Crassula ovata (Jade Plant or Jade Tree)
- Toxicity: unknown.
- Toxic part: all parts of the plant.
- Symptoms: ingestion may cause symptoms of gastrointestinal distress, including nausea, vomiting and, in some cases, lethargy and poor coordination.
- Dracaena the most common (Madagascar dragon tree or Dragon tree)
- Toxicity: Saponins.
- Toxic part: the whole plant is toxic.
- Symptoms: ingestion may cause symptoms such as vomiting, salivation due to mucosal irritation, weakness and in rare cases diarrhea.
- Cyclamen (Alpine Violet, Persian Violet, and Sowbread)
- Toxicity: Saponins.
- Toxic part: high concentration in roots.
- Symptoms: ingestion may cause gastrointestinal irritation, including nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. In more severe cases, convulsions in high doses.
- Sansevieria trifasciata (Snake Plant, Mother-in-law’s tongue)
- Toxicity: Saponins.
- Toxic part: Whole plant.
- Symptoms: Ingestion of this plant may cause nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, as well as mild irritation of the mouth and throat.

Outdoor toxic plants
- Toxicity: Cardiotoxic glycosides (digoxin, digitoxin, oleandrin).
- Toxic part: all parts of these plants are toxic.
- Symptoms: but can also cause symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, weakness, vision changes, confusion, and significant cardiac disturbances that can be fatal. The main action of cardiac glycosides is on the cardiovascular system and can cause arrhythmias leading to severe complications or death.

- Azalea
- Rhododendron
- Toxicity: Glycosides grayanotoxins.
- Toxic part: all parts of the plant.
- Symptoms: May cause symptoms such as excessive salivation, vomiting, diarrhea, weakness, central nervous system depression, hypotension and, in severe cases, coma or death due to cardiovascular and respiratory involvement.
- Ricinus communis (Castor oil plant)
- Toxicity: Ricin.
- Toxic part: especially concentrated in the seeds.
- Symptoms: Ingestion of the seeds can cause severe symptoms including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever, hypotension and can cause multi-organ failure. Even a small amount of seeds can be lethal to an adult or child if chewed and ingested.
- Asparagus setaceus (Asparagus Fern o Plumosus)
- Toxicidad: Saponins.
- Toxic part: whole plant.
- Symptoms: Ingestion may cause abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. Skin contact may cause dermatitis or irritation, especially due to its thorns and sap.
- Taxus (Yew)
- Toxicity: Taxine.
- Toxic part: needles, seeds and bark.
- Symptoms: can cause symptoms such as dizziness, dry mouth, dilated pupils, weakness, breathing difficulties, tachycardia or bradycardia, and can lead to cardiac arrest. The toxicity of yew is such that even a small amount can result in severe poisoning.
- Hydrangea
- Sambucus (Elderberry)
- Toxicity: Cyanogenic glycosides (hydrangine, samabunigrin).
- Toxic part: all parts of the plant, especially leaves and flowers, in the case of elderberry mainly leaves, branches, seeds and roots, being the immature parts of the plant and especially the green berries the most toxic.
- Symptoms: Ingestion may cause symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, severe diarrhea. In more severe cases, it may produce dizziness and confusion due to the release of cyanide in the body.
- Wisteria
- Toxicity: Wisteria glycosides and lectins.
- Toxic part: all its parts, being especially toxic the seeds and pods.
- Symptoms: ingestion may cause nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea and, in severe cases, nervous system depression that could lead to confusion or convulsions.
- Iris (Lilies)
- Toxicity: iridoid glycosides.
- Toxic part: especially the roots.
- Symptoms: may cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Contact with sap may also cause skin and eye irritation.

- Narcissus (Narciso)
- Toxicity: Licorin.
- Toxic part: the whole plant, especially the bulbs.
- Symptoms: Ingestion may cause vomiting, nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain, and in severe cases, depression of the central nervous system, leading to lethargy or convulsions. Skin contact may, in rare cases, cause dermatological irritation in sensitive dogs and cats.
-
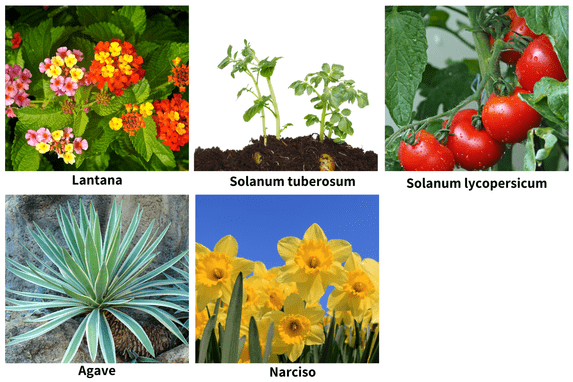
Lantana (Shrub Verbena, Spanish Flag)
- Toxicity: Triterpenoids Lantadene A and B.
- Toxic part: especially in its green berries. Leaves and flowers may also be irritating if ingested.
- Symptoms: ingestion may cause symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, weakness, dilated pupils, and in severe cases, liver failure.
- Nightshade (Best known are potato and tomato)
- Toxicity: Solanine.
- Toxic part: the green part of the plant, leaves, stem and unripe berries. Toxicity can vary significantly among species within this large and diverse genus.
- Symptoms: May cause symptoms such as headache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, drowsiness, confusion and, in severe cases, respiratory distress and heart failure.
- Agaves
- Toxicity: They are not particularly toxic. Although some species contain calcium oxalate crystals.
- Toxic part: The sap, although the associated risks tend to be more from physical contact, as they have rather hard leaves ending in a sharp spine, sometimes accompanied by other small spines on the edges.
- Symptoms: The sap may contain irritant compounds which, if they come into contact with the skin or mucous membranes, can cause irritation, contact dermatitis, and in cases of eye contact, pain and possible eye damage. In addition, the sharp points and cutting edges of the leaves can cause serious physical injury.
Not all plants are equally dangerous, and the severity of their effect depends on the dose. However, some can be lethal. Therefore, we have created a special post on toxic plants for dogs and cats, to warn you about the risks of certain plants and offer preventive advice to avoid exposure and how to proceed in case of poisoning.
In Balmesvet, we have a veterinary emergency service available 24 hours a day, 365 days a year, in Barcelona. We know how crucial quick and effective care is in emergency situations. If you have a veterinary emergency, such as a possible poisoning or any other serious incident, we recommend that you call us immediately at 931173173 while you are on your way to our veterinary hospital.
- Toxicity: Cardiotoxic glycosides (digoxin, digitoxin, oleandrin).
- Toxic part: all parts of these plants are toxic.
- Symptoms: but can also cause symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, weakness, vision changes, confusion, and significant cardiac disturbances that can be fatal. The main action of cardiac glycosides is on the cardiovascular system and can cause arrhythmias leading to severe complications or death.

- Azalea
- Rhododendron
- Toxicity: Glycosides grayanotoxins.
- Toxic part: all parts of the plant.
- Symptoms: May cause symptoms such as excessive salivation, vomiting, diarrhea, weakness, central nervous system depression, hypotension and, in severe cases, coma or death due to cardiovascular and respiratory involvement.
- Ricinus communis (Castor oil plant)
- Toxicity: Ricin.
- Toxic part: especially concentrated in the seeds.
- Symptoms: Ingestion of the seeds can cause severe symptoms including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever, hypotension and can cause multi-organ failure. Even a small amount of seeds can be lethal to an adult or child if chewed and ingested.
- Asparagus setaceus (Asparagus Fern o Plumosus)
- Toxicidad: Saponins.
- Toxic part: whole plant.
- Symptoms: Ingestion may cause abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. Skin contact may cause dermatitis or irritation, especially due to its thorns and sap.
- Taxus (Yew)
- Toxicity: Taxine.
- Toxic part: needles, seeds and bark.
- Symptoms: can cause symptoms such as dizziness, dry mouth, dilated pupils, weakness, breathing difficulties, tachycardia or bradycardia, and can lead to cardiac arrest. The toxicity of yew is such that even a small amount can result in severe poisoning.
- Hydrangea
- Sambucus (Elderberry)
- Toxicity: Cyanogenic glycosides (hydrangine, samabunigrin).
- Toxic part: all parts of the plant, especially leaves and flowers, in the case of elderberry mainly leaves, branches, seeds and roots, being the immature parts of the plant and especially the green berries the most toxic.
- Symptoms: Ingestion may cause symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, severe diarrhea. In more severe cases, it may produce dizziness and confusion due to the release of cyanide in the body.
- Wisteria
- Toxicity: Wisteria glycosides and lectins.
- Toxic part: all its parts, being especially toxic the seeds and pods.
- Symptoms: ingestion may cause nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea and, in severe cases, nervous system depression that could lead to confusion or convulsions.
- Iris (Lilies)
- Toxicity: iridoid glycosides.
- Toxic part: especially the roots.
- Symptoms: may cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Contact with sap may also cause skin and eye irritation.

- Narcissus (Narciso)
- Toxicity: Licorin.
- Toxic part: the whole plant, especially the bulbs.
- Symptoms: Ingestion may cause vomiting, nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain, and in severe cases, depression of the central nervous system, leading to lethargy or convulsions. Skin contact may, in rare cases, cause dermatological irritation in sensitive dogs and cats.
-
Lantana (Shrub Verbena, Spanish Flag)
- Toxicity: Triterpenoids Lantadene A and B.
- Toxic part: especially in its green berries. Leaves and flowers may also be irritating if ingested.
- Symptoms: ingestion may cause symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, weakness, dilated pupils, and in severe cases, liver failure.
- Nightshade (Best known are potato and tomato)
- Toxicity: Solanine.
- Toxic part: the green part of the plant, leaves, stem and unripe berries. Toxicity can vary significantly among species within this large and diverse genus.
- Symptoms: May cause symptoms such as headache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, drowsiness, confusion and, in severe cases, respiratory distress and heart failure.
- Agaves
- Toxicity: They are not particularly toxic. Although some species contain calcium oxalate crystals.
- Toxic part: The sap, although the associated risks tend to be more from physical contact, as they have rather hard leaves ending in a sharp spine, sometimes accompanied by other small spines on the edges.
- Symptoms: The sap may contain irritant compounds which, if they come into contact with the skin or mucous membranes, can cause irritation, contact dermatitis, and in cases of eye contact, pain and possible eye damage. In addition, the sharp points and cutting edges of the leaves can cause serious physical injury.

Not all plants are equally dangerous, and the severity of their effect depends on the dose. However, some can be lethal. Therefore, we have created a special post on toxic plants for dogs and cats, to warn you about the risks of certain plants and offer preventive advice to avoid exposure and how to proceed in case of poisoning.
In Balmesvet, we have a veterinary emergency service available 24 hours a day, 365 days a year, in Barcelona. We know how crucial quick and effective care is in emergency situations. If you have a veterinary emergency, such as a possible poisoning or any other serious incident, we recommend that you call us immediately at 931173173 while you are on your way to our veterinary hospital.
- Aconitum (Monkshood, Queen of poisons, Wolfsbane)
- Toxicity: Aconitine.
- Toxic part: whole plant.
- Symptoms: Ingestion can rapidly cause severe symptoms, including burning in the mouth and throat, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, blurred vision, weakness, respiratory distress, heart disturbances and convulsions, and may be fatal. Skin contact may cause numbness and tingling due to absorption of toxins.
- Atropa belladonna (Deadly nightshade, belladonna)
- Toxicity: tropane alkaloids (atropine, hyoscyamine and scopolamine).
- Toxic part: all highly toxic parts.
- Symptoms: ingestion may cause dry mouth, difficulty swallowing, blurred vision, dilated pupils, tachycardia, fever, hallucinations and convulsions, leading in severe cases to coma or death. In contact with skin may cause skin irritation or allergic reactions in sensitive dogs and cats.
- Hemlock (Conium maculatum, Poison hemlock)
- Toxicity: Conine.
- Toxic part: all parts of the plant, with a higher concentration in the seeds and root.
- Symptoms: Ingestion of hemlock can cause severe symptoms including muscle tremors, progressive weakness, paralysis of the nervous system, and can be fatal if respiratory muscles are affected, leading to asphyxiation.
- Delphinium (Lark’s Heel, Lark’s Claw and Knight’s Spur)
- Laburnum anagyroides (Golden chain tree or Golden rain tree)
- Lupinus (Bluebonnet, lupin or lupine)
- Toxicity: Alkaloids (Delphinin, Cytonin, Quinolizidine).
- Toxic part: all parts of the plant, in some cases especially the seeds.
- Symptoms: Ingestion may cause symptoms such as gastrointestinal irritability, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, weakness, drowsiness, convulsions, respiratory distress, and in severe cases, coma, paralysis, heart rhythm disturbances and heart failure which can be fatal.
- Papaver somniferum (Opium Poppy)
-
- Toxicity: Opiate alkaloids (such as morphine and codeine).
- Toxic part: All parts of the plant have toxic potential, but the alkaloids are mainly concentrated in the latex of the immature capsules (poppies).
-
- Digitalis purpurea (Foxglove, fairy glove)
- Nerium oleander (Oleander)
- Toxicity: Cardiotoxic glycosides (digoxin, digitoxin, oleandrin).
- Toxic part: all parts of these plants are toxic.
- Symptoms: but can also cause symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, weakness, vision changes, confusion, and significant cardiac disturbances that can be fatal. The main action of cardiac glycosides is on the cardiovascular system and can cause arrhythmias leading to severe complications or death.

- Azalea
- Rhododendron
- Toxicity: Glycosides grayanotoxins.
- Toxic part: all parts of the plant.
- Symptoms: May cause symptoms such as excessive salivation, vomiting, diarrhea, weakness, central nervous system depression, hypotension and, in severe cases, coma or death due to cardiovascular and respiratory involvement.
- Ricinus communis (Castor oil plant)
- Toxicity: Ricin.
- Toxic part: especially concentrated in the seeds.
- Symptoms: Ingestion of the seeds can cause severe symptoms including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever, hypotension and can cause multi-organ failure. Even a small amount of seeds can be lethal to an adult or child if chewed and ingested.
- Asparagus setaceus (Asparagus Fern o Plumosus)
- Toxicidad: Saponins.
- Toxic part: whole plant.
- Symptoms: Ingestion may cause abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. Skin contact may cause dermatitis or irritation, especially due to its thorns and sap.
- Taxus (Yew)
- Toxicity: Taxine.
- Toxic part: needles, seeds and bark.
- Symptoms: can cause symptoms such as dizziness, dry mouth, dilated pupils, weakness, breathing difficulties, tachycardia or bradycardia, and can lead to cardiac arrest. The toxicity of yew is such that even a small amount can result in severe poisoning.
- Hydrangea
- Sambucus (Elderberry)
- Toxicity: Cyanogenic glycosides (hydrangine, samabunigrin).
- Toxic part: all parts of the plant, especially leaves and flowers, in the case of elderberry mainly leaves, branches, seeds and roots, being the immature parts of the plant and especially the green berries the most toxic.
- Symptoms: Ingestion may cause symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, severe diarrhea. In more severe cases, it may produce dizziness and confusion due to the release of cyanide in the body.
- Wisteria
- Toxicity: Wisteria glycosides and lectins.
- Toxic part: all its parts, being especially toxic the seeds and pods.
- Symptoms: ingestion may cause nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea and, in severe cases, nervous system depression that could lead to confusion or convulsions.
- Iris (Lilies)
- Toxicity: iridoid glycosides.
- Toxic part: especially the roots.
- Symptoms: may cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Contact with sap may also cause skin and eye irritation.

- Narcissus (Narciso)
- Toxicity: Licorin.
- Toxic part: the whole plant, especially the bulbs.
- Symptoms: Ingestion may cause vomiting, nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain, and in severe cases, depression of the central nervous system, leading to lethargy or convulsions. Skin contact may, in rare cases, cause dermatological irritation in sensitive dogs and cats.
-
Lantana (Shrub Verbena, Spanish Flag)
- Toxicity: Triterpenoids Lantadene A and B.
- Toxic part: especially in its green berries. Leaves and flowers may also be irritating if ingested.
- Symptoms: ingestion may cause symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, weakness, dilated pupils, and in severe cases, liver failure.
- Nightshade (Best known are potato and tomato)
- Toxicity: Solanine.
- Toxic part: the green part of the plant, leaves, stem and unripe berries. Toxicity can vary significantly among species within this large and diverse genus.
- Symptoms: May cause symptoms such as headache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, drowsiness, confusion and, in severe cases, respiratory distress and heart failure.
- Agaves
- Toxicity: They are not particularly toxic. Although some species contain calcium oxalate crystals.
- Toxic part: The sap, although the associated risks tend to be more from physical contact, as they have rather hard leaves ending in a sharp spine, sometimes accompanied by other small spines on the edges.
- Symptoms: The sap may contain irritant compounds which, if they come into contact with the skin or mucous membranes, can cause irritation, contact dermatitis, and in cases of eye contact, pain and possible eye damage. In addition, the sharp points and cutting edges of the leaves can cause serious physical injury.

Not all plants are equally dangerous, and the severity of their effect depends on the dose. However, some can be lethal. Therefore, we have created a special post on toxic plants for dogs and cats, to warn you about the risks of certain plants and offer preventive advice to avoid exposure and how to proceed in case of poisoning.
In Balmesvet, we have a veterinary emergency service available 24 hours a day, 365 days a year, in Barcelona. We know how crucial quick and effective care is in emergency situations. If you have a veterinary emergency, such as a possible poisoning or any other serious incident, we recommend that you call us immediately at 931173173 while you are on your way to our veterinary hospital.
Compartir

